HEART

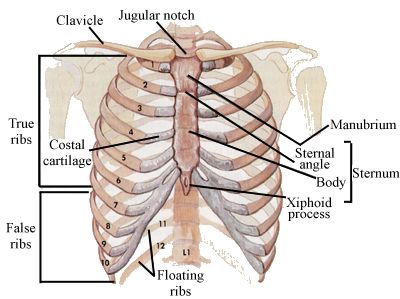
INTRODUCTION Mediastinum(plural-mediastina)(Latin intermediate ) is the middle space left in the thoracic cavity in between the lungs. Its most important content is the heart, enclosed in the pericardium in the middle part of the inferior mediastinum or the middle mediastinum. SUPERIOR AND INFERIOR MEDIASTINA For descriptive purpose, the mediastina is divided into superior mediastinum and the inferior mediastinum. Fig.: Subdivisions of the mediastinum SUPERIOR MEDIASTINUM Boundaries Anteriorly: Manubrium sterni Posteriorly: Upper four thoracic vertebrae Superiorly: Plane of the thoracic inlet Inferiorly: An imaginary plane passing through the sternal angle in front, and the lower border of the body of the fourth thoracic vertebra behind. On each side: Mediastinal pleura Contents 1. Trachea and esophagus. 2. Muscles: Orig