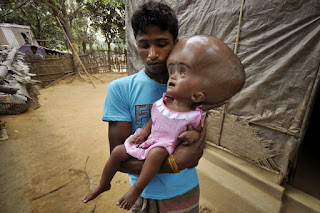
HYDROCEPHALUS
HYDROCEPHALUS
Term ‘hydro’
meaning water and ‘cephalus’ referring to the head.
Hydrocephalus
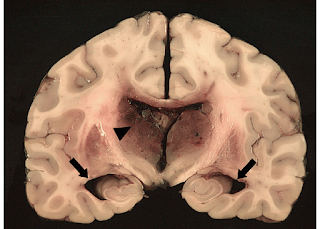
is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs
within the cavities of the brain.
CSF has 3
crucial functions in our body-
1.
It acts as a shock absorber for the brain and spinal cord
2.
It acts as a vehicle for transporting nutrients in the brain and removing
waste.
3.
It flows between the cranium and spine to regulate changes in pressure
within the brain.
This
accumulation of CSF causes increased pressure inside the skull. Hydrocephalus
can occur due to birth defects or can be acquired later in life.
The 4 types of
hydrocephalous are communicating, non-communicating, ex-vacuo, and normal
pressure.
SYMPTOMS
The signs and
symptoms of hydrocephalus may vary by age of onset.
In infants CSF
builds up in CNS, causing the signs and symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants
include:
·
Vomiting
·
Sleepiness
·
Irritability
·
Poor feeding
·
Seizures
·
Eyes fixed downwards
·
Deficits in muscle tone and strength
·
Poor response to touch
·
Poor growth
CHANGES IN
HEAD
·
An unusually large head
·
A bulging or tense soft spot on the top of the head
·
A rapid increase in size of the head
YOUNG & MIDDLE-AGED ADULTS
Common sign
and symptoms in this age group include:
·
Headache
·
Loss of coordination
·
Decline in memory, concentration, and other thinking skills
·
Frequent urge of urination
·
Impaired vision
·
Lethargy
OLDER ADULTS
·
Loss of coordination
·
Loss of bladder control
· loss of reasoning skills
·
Memory loss
CAUSES
There are two
types of causes for hydrocephalus- i) CONGENITAL ii) ACQUIRED
CONGENITAL
Congenital
hydrocephalus is present in the infant prior to birth in the uterus during fetal
development. Most common cause of congenital hydrocephalus is AQUEDUCTAL
STENOSIS (narrowing of the aqueduct of Sylvius), which occurs when the narrow
passage between the 3rd and 4th ventricle in the brain is
blocked to allow sufficient CSF to drain. Therefore, fluid accumulates in upper
ventricles causing hydrocephalus.
Other possible
causes for hydrocephalus are neural tube defects, arachnoid cysts, Dandy walker
syndrome and Arnold-Chiari malformation.
About 80-90%
of fetuses with spina-bifida often associated with a meningocele or
myelomeningocele develop hydrocephalus.
ACQUIRED
This condition
hydrocephalus is acquired as a consequence of CNS infection, meningitis, brain
tumors, head trauma, toxoplasmosis or intracranial hemorrhage (subarachnoid
or intraparenchymal) and is usually painful.
Excessive CSF
in the ventricles occurs for one of the following reasons:
i)
Obstruction- The most common problem is a partial obstruction of the normal flow of CSF, either from one ventricle to another or from the ventricles
to other spaces around the brain.
ii)
Poor absorption- Less common problem is with the mechanism that enables
the blood vessels to absorb CSF. This is often related to inflammation of the brain
tissue from disease or injury.
iii)
Overproduction- Rarely, CSF is created to move quickly than it can be
absorbed.
DIAGNOSIS
Diagnosis of
hydrocephalus is usually based on
·
A general physical exam
·
Neurological exam
·
Brain imaging test
NEUROLOGICAL EXAM
Type of
neurological exam depends on a person’s age.
Neurologist
may conduct a relative simple test to judge muscle condition, movement, wellbeing
& Senses function.
BRAIN IMAGING
Brain imaging
tests can show enlarged ventricles caused by the accumulation of excess of CSF. It
is also used to identify the underlying causes of hydrocephalus.
Imaging test
may include:
a. ULTRASOUND-
It is often
used for an initial assessment for infants because it’s a relatively simple,
low-risk procedure. The ultrasound is placed over the fontanel spot on the top
of the baby’s head. It can also detect the hydrocephalus prior to birth in the mother’s
womb during regular parental examinations.
b. MRI (MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING)-
This test is
painless, but it is noisy and requires lying still.
Children may
need a mild sedative for MRI scans.
c.
COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY (CT SCANS)
Scanning is
painless and quick, but this test also requires lying still so child usually
receives mild sedative.
Drawbacks of
CT Scanning includes less detailed images than an MRI, and exposure to small
amount of radiation.
TREATMENT
There are 2
surgical treatments for hydrocephalus-
SHUNT
Most common
treatment for hydrocephalus is the surgical insertion of a drainage tube called
shunt between the brain ventricles and abdominal cavity.
The shunt is a flexible narrow tube with a valve that keep fluids from the brain flowing in the right
direction at a proper rate.
One end of the
tubing is usually placed in one of the ventricles of the brain, then the tubing is
tunneled under the skin to another part of the body where the excess
cerebrospinal fluid can be more easily absorbed such as abdomen or chambers of
heart.
EXTERNAL VENTRICULAR DRAIN (ETV) OR ENDOSCOPIC THIRD VENTRICULOSTOMY
In ETV the surgeon uses a small video camera to have a direct vision inside the brain. Then
he makes a hole in the bottom of one of the ventricles or between the ventricles
to enable CSF to flow out of the brain.
Departments
that treat this condition is- NEUROLOGY
NEUROSURGERY




Comments
Post a Comment